As part of the EIA, numerical modelling has been used to investigate the hydrodynamic action and the plume dispersion due to dredging and reclamation works in Addu atoll. Tides, waves and wind are the factors that drive the water flow which results in seabed morphological changes, exerting forces on marine structures and are responsible for the motion of sediment plumes during dredging and reclamation works.
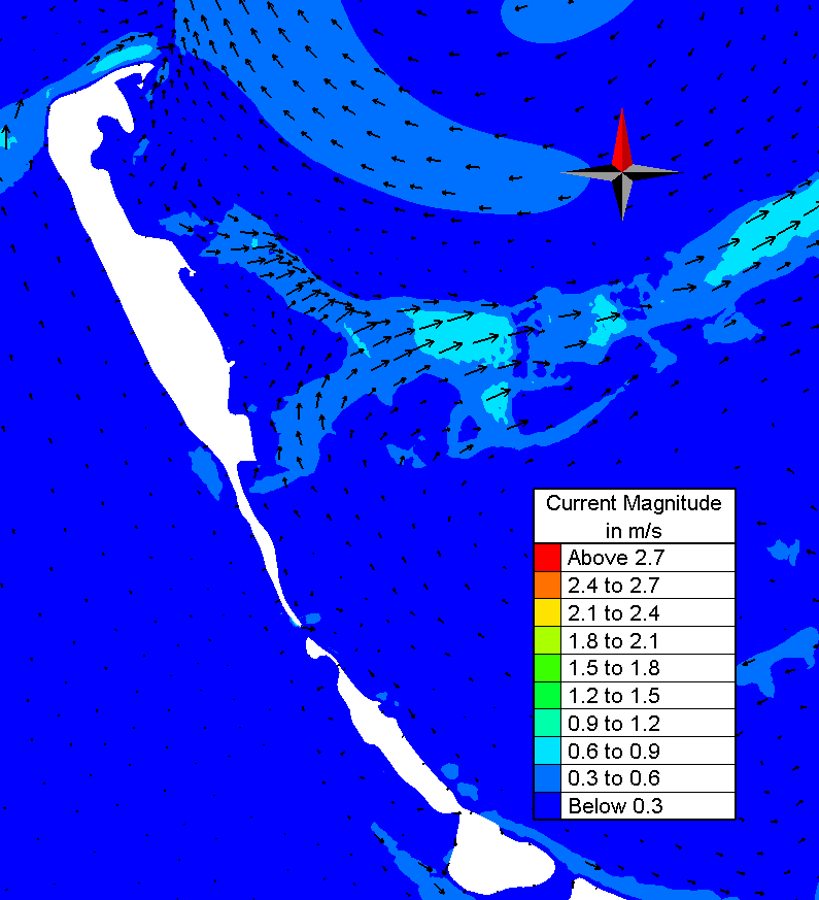
Three scenarios with regards to hydrodynamic forcing have been investigated: wet-monsoon, dry-monsoon and non-monsoon periods. Characteristic results of expected flow patterns during wet monsoon can be seen in the plots below.

Representative plot of current pattern during wet monsoon for existing condition of Addu atoll
Moreover, plume dispersion during dredging and reclamation has been investigated for all the hydrodynamic scenarios in each of the approved borrow areas within the atoll.
The average concentration during dredging in the borrow area located in the south side inside the atoll can be seen in the following plots during wet-monsoon, dry-monsoon and non-monsoon periods.

Average concentration for dredging at Borrowing Area 1 during wet-monsoon

Average concentration for dredging at Borrowing Area 1 during dry-monsoon

Average concentration for dredging at Borrowing Area 1 during non-monsoon
You can read more on the numerical modelling studies in the EIA documents here.